What Are Warehouse Robots & How They Work
Picture a warehouse on a Monday morning: orders are piling up, shelves are stacked high, and workers are rushing to keep up. Every minute counts, and one mistake can ripple across the entire operation.
This is the reality for modern warehouses, where growing SKUs, labor shortages, and fast fulfillment demand push traditional methods to their limits. That’s where warehouse robots, particularly those in Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS), step in, reshaping the way warehouses store, pick, and deliver goods.
But what exactly are these robots, how do they operate, and why are they becoming the backbone of next-generation warehouse automation?
What Are Warehouse Robots?
Warehouse robots are automated machines that move, store, and retrieve goods within warehouse environments. They combine mobility, sensing, and intelligent software to execute tasks such as picking, replenishment, sorting, and storage with minimal human input.
Over the past two decades, warehouse robotics has evolved from fixed, rail-based cranes to modular, software-driven systems capable of adapting to different warehouse layouts and workflows. Today’s robots don’t simply move goods; they collaborate with digital systems to make the most of every available space and every moment of operation.
Key Categories of Warehouse Robots
While many warehouse robots are designed for specific tasks, true operational efficiency comes from how these robots collaborate as a system. Below are the key categories.
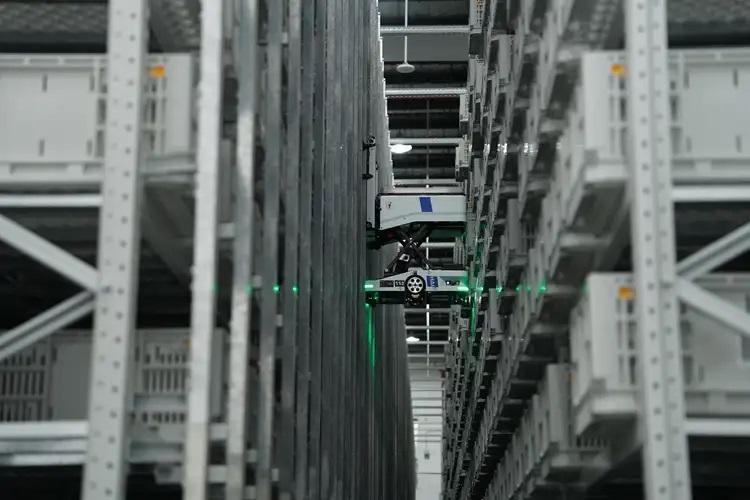
1. Tote-Handling Robots
Tote-handling robots are designed to automate the movement of totes or trays between storage racks and picking stations.
-
How they work: They travel along aisles using forks or robotic arms to pick totes from storage racks and deliver them to ports or workstations. In HaiPick Systems, HaiPick Robots such as the award-winning HaiPick A42 series, A3S, and HaiClimber efficiently handle tote picking and put-away tasks across diverse warehouse scenarios, adapting to different heights, load types, and operational needs.
-
Where they shine: Ideal for small to medium-sized items (electronics, apparel, grocery, healthcare, spare parts) and high-SKU environments where manual picking becomes inefficient.
-
Key benefits:
-
Flexible to pick and put away totes from high-bay racks, maximizing vertical space and storage density.
-
Enables real-time retrieval of any SKU, at any level.
-
Scales easily by adding robots or racks without system downtime.
-
These robots form the “hands” of the ASRS, enabling high-density goods-to-person workflows with speed and precision.

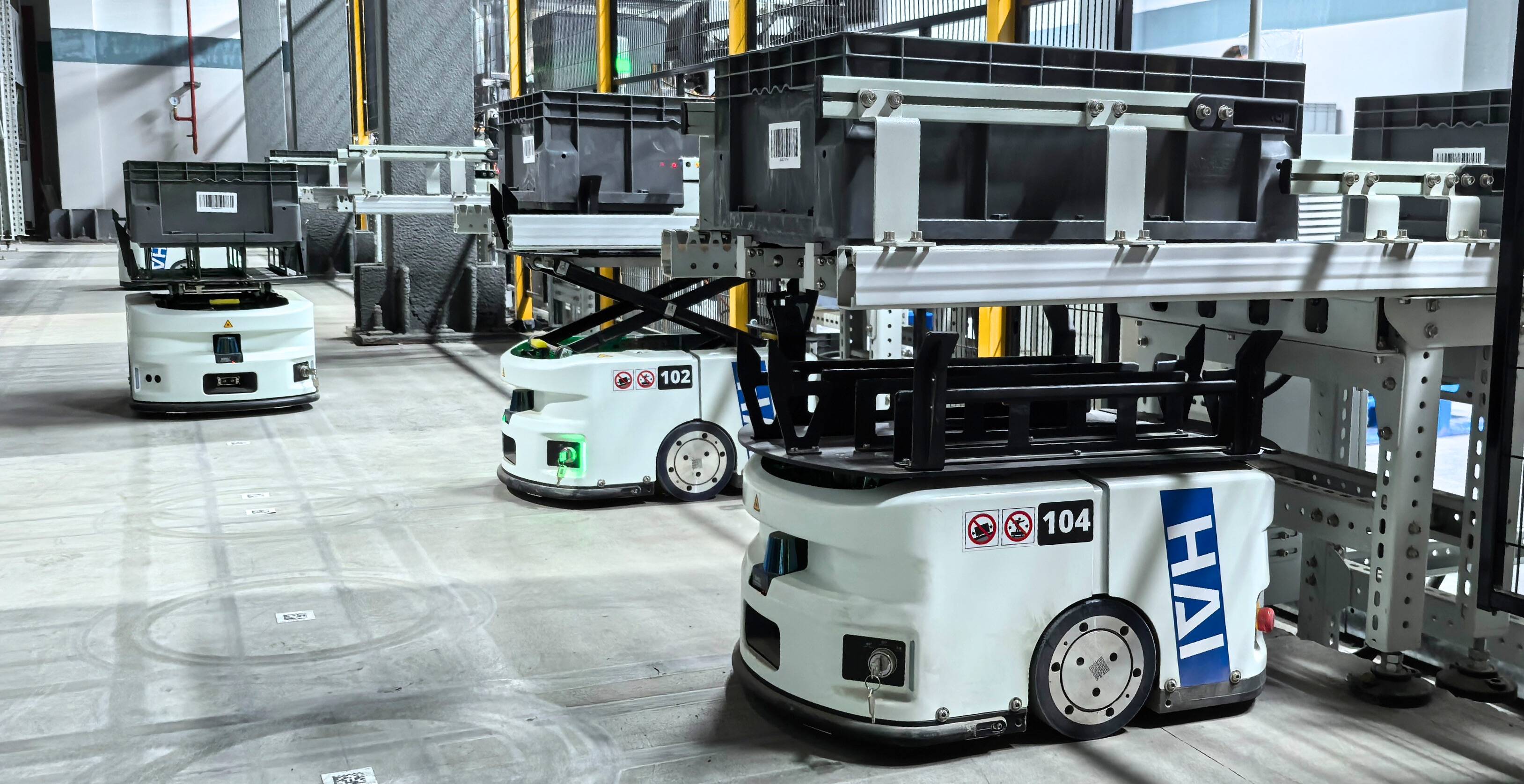
2. Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs play a crucial role in horizontal transportation, bridging zones like inbound, packing, and outbound.
-
How they work: AMRs are compact, self-guided robots that move goods horizontally across warehouse zones. Using sensors and real-time mapping, they navigate freely without fixed paths, transporting totes or cartons between storage and picking areas. In HaiPick Systems, AMRs collaborate seamlessly with HaiPick Robots to deliver goods efficiently.
-
Where they shine: AMRs are compact and agile, moving easily through tight spaces and adapting quickly to layout changes. When working alongside Automated Case-Handling Mobile Robots (ACRs), AMRs handle short-distance transfers while ACRs manage vertical storage, combining speed and density for higher overall efficiency.
-
Key benefits:
-
Layout flexibility; no fixed infrastructure.
-
Faster horizontal transport and reduced idle time.
-
Compact design for better space utilization.
-
By linking automated and semi-automated areas, AMRs make the entire operation more cohesive and scalable.

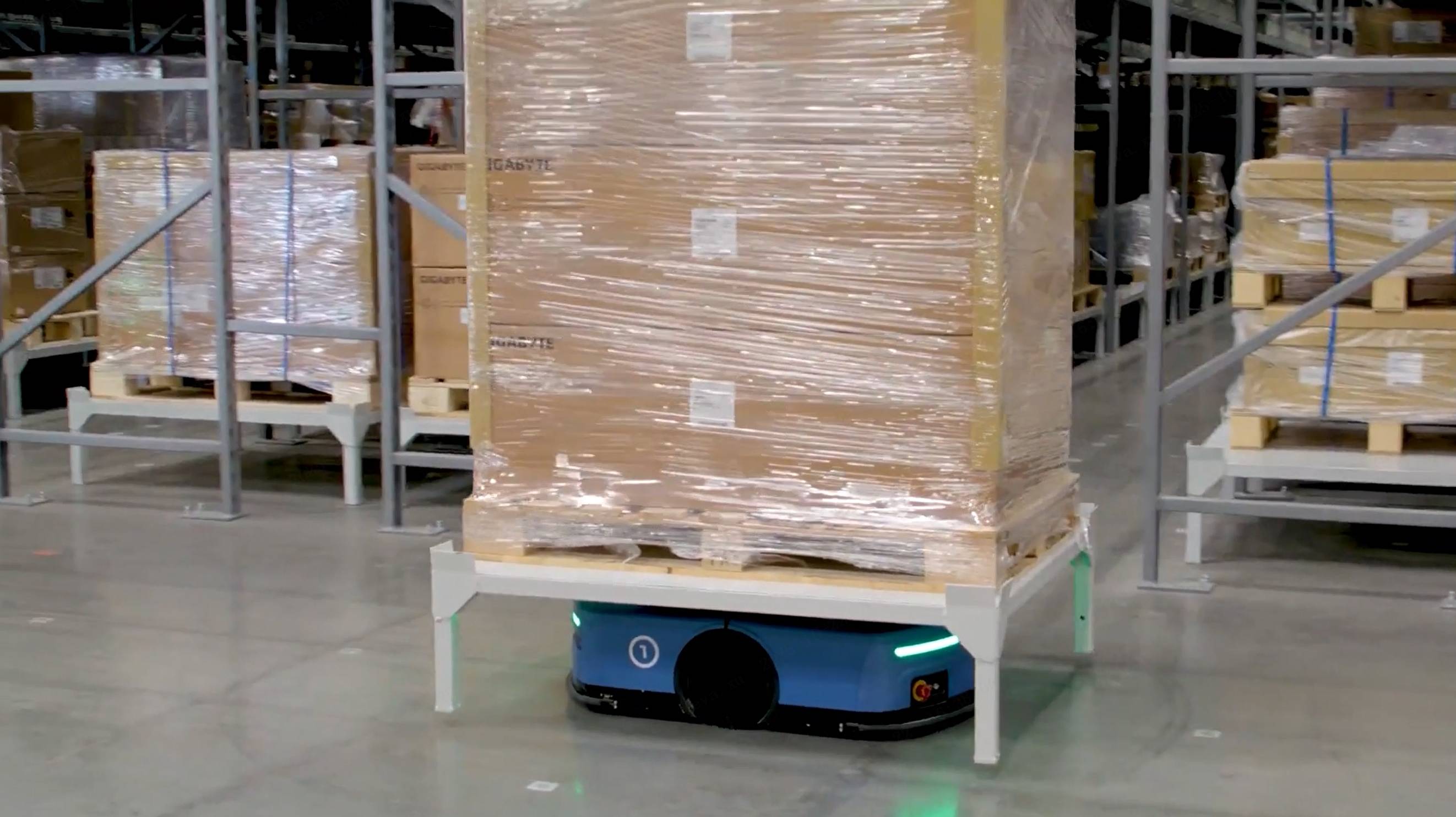
3. Pallet-Handling Robots
For large or heavy goods, pallet-handling robots provide automated movement and storage at the pallet level.
-
How they work: They automate traditional forklift operations by lifting, transporting, and stacking pallets between inbound, storage, and outbound areas. Integrated with warehouse software, these robots can coordinate with tote-handling systems to support mixed-case or full-pallet operations within the same facility.
-
Where they shine: Distribution centers, food & beverage, or manufacturing, where mixed-load handling is required.
-
Key benefits:
-
Safer handling of bulky items.
-
Can be integrated with tote-based systems.
-
They streamline heavy-load handling and seamlessly connect with tote-based systems, enabling a unified and efficient warehouse flow.

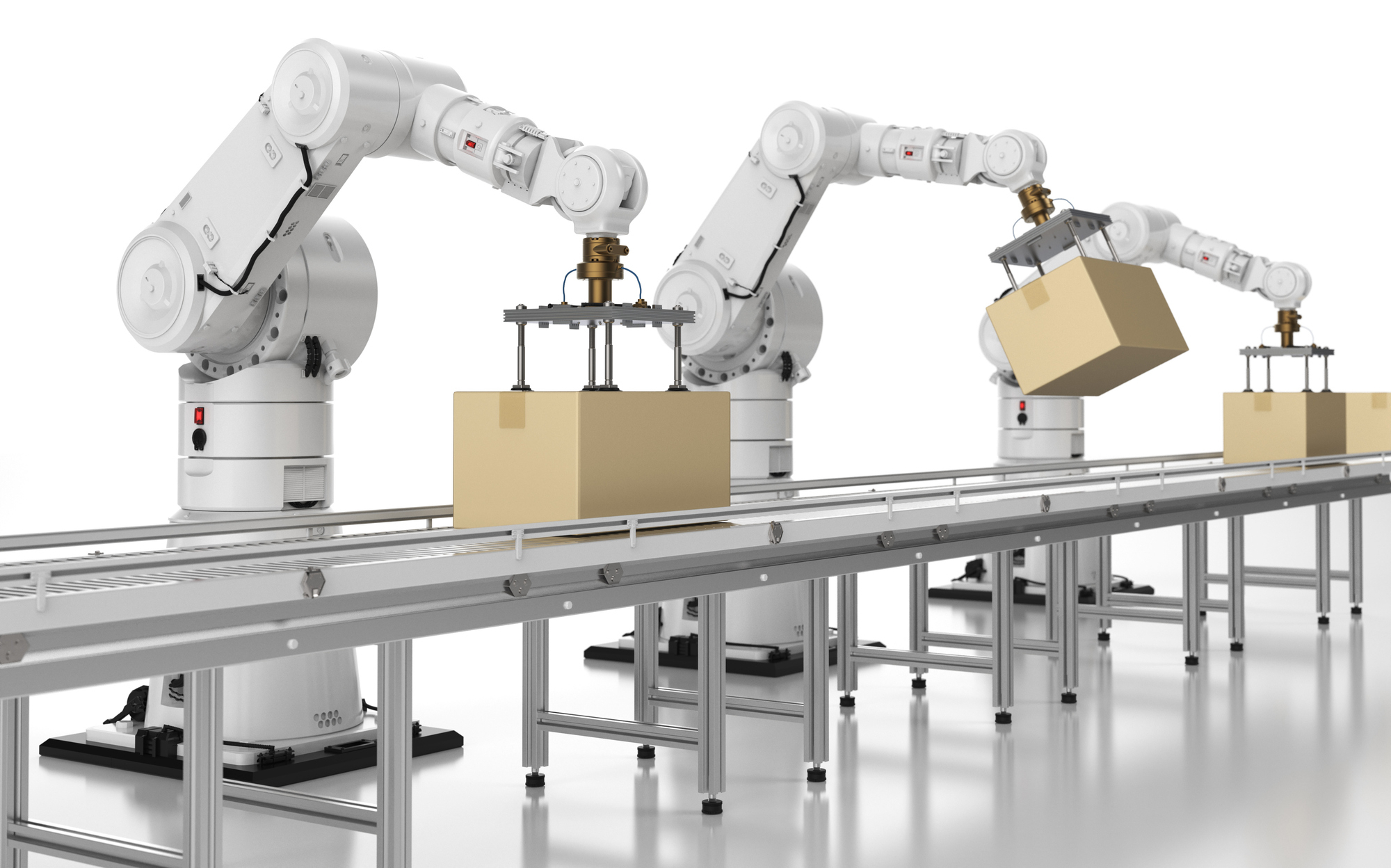
4. Item-Handling Robots
Item-handling robots are best suited for high-SKU, item-level picking environments such as e-commerce, healthcare, and retail warehouses.
-
How they work: These robots use robotic arms with advanced vision systems and grippers to pick individual items from totes or conveyors. AI-based vision recognition allows them to handle a wide variety of products, from boxes and pouches to irregularly shaped goods.
-
Where they shine: They excel in automating the final stage of order fulfillment, reducing manual touches, and ensuring consistent accuracy for single-item picking.
-
Key benefits:
-
Handles high-SKU, item-level picking efficiently
-
Reduces labor intensity and human errors
-
Item-handling robots ensure precise and human-free item-level picking, eliminating issues caused by worker fatigue, shift changes, and picking errors.

How Robots Collaborate with Software?
What makes warehouse robotics powerful isn’t just the hardware; it’s the system logic behind how robots communicate, coordinate, and optimize tasks.
At the top, the Warehouse Management System (WMS) decides what needs to happen, managing inventory, orders, and priorities. The Warehouse Control System (WCS) then translates those decisions into how it happens, orchestrating robots, conveyors, ports, and stations in real time.
In a Hai Robotics system, this orchestration is powered by HaiQ's Equipment Scheduling System (ESS), the smart software suite that ensures:
-
Optimal task assignment across multiple robots.
-
Route optimization for the shortest retrieval time.
-
Dynamic adjustment to workload peaks or equipment status.
This creates a self-balancing network: every robot acts as a node within a synchronized, data-driven ecosystem.
The Real-World Workflow
Below is a simplified flow of how a modern warehouse with robots operates:
-
Inbound: AMRs or Conveyors transport incoming goods from the dock to a receiving zone. After initial checks and dencanting, totes or cases are passed to the ASRS buffer.
-
Storage/Put-away: ACRs such as HaiPick Robots store totes or cases in designated rack locations. The storage logic is dynamic, so layout adjustments or re-slotting happen based on usage patterns.
-
Order Picking/Retrieval: When orders come in, robots retrieve the relevant totes or items and deliver them to workstation ports. Transfer robots or HaiPort interfaces manage tote exchanges.
-
Sorting & Packing: After picking, items are sorted and consolidated, then sent via AMRs or conveyors to packing zones.
-
Outbound/Shipping: Packed orders are routed to shipping zones or dock buffers for dispatch.
At each stage, smart software like HaiQ tracks real-time status, adjusts robot tasks, and updates inventory. This continuous feedback loop ensures consistent throughput and adaptability. Learn more about how HaiQ optimizes warehouse operations and boosts efficiency.
Benefits Beyond Labor Savings
While labor reduction is often the first benefit that comes to mind, the real advantages of a well-integrated ASRS system (especially HaiPick Systems’ architecture) are deeper:
-
Higher Storage Density: Robots can reach higher rack levels and operate in tighter spaces, enabling warehouses to maximize vertical storage and make full use of existing volume. Read more about maximizing density and flexibility.
-
System Flexibility & Scalability: The modular design of HaiPick Systems allows gradual scaling based on business needs: add more robots, workstations, or rack modules without a complete redesign.
-
Extensive Compatibility: Mixed-type picking is also supported to handle a wide range of product sizes and weights within a single system. For example, GIGABYTE’s project with HaiPick System 2 demonstrates handling both individual-item (tote) and bulk/palletized goods within a single storage zone, easily accommodating a wide range of product sizes and weights.
-
Improved Throughput and Accuracy: Optimized and synchronized robot movements reduce cycle times and errors, while efficient multitote paths and smooth flow control ensure high operational performance.
-
Resilience to Change: With dynamic task assignment and route adjustment, the system can adapt to demand surges or layout changes, avoiding bottlenecks while maintaining operational continuity.
Looking Ahead
Warehouse robots are evolving from single-task performers into system-level collaborators. As the logistics industry embraces flexibility and intelligence, modular robotics is setting new standards for what ASRS can achieve. The future of warehousing will not be defined by how many robots are deployed, but by how well they work together with humans, with software, and with space itself.
Curious how warehouse robots can modernize your warehouse? Explore HaiPick Systems to see how flexible, modular robotics can transform your operations.