The Ultimate Guide to Warehouse Order Picking: Processes, Strategies, and Best Practices
Master warehouse order picking with our comprehensive guide. Learn strategies, systems, and best practices to improve efficiency and accuracy.
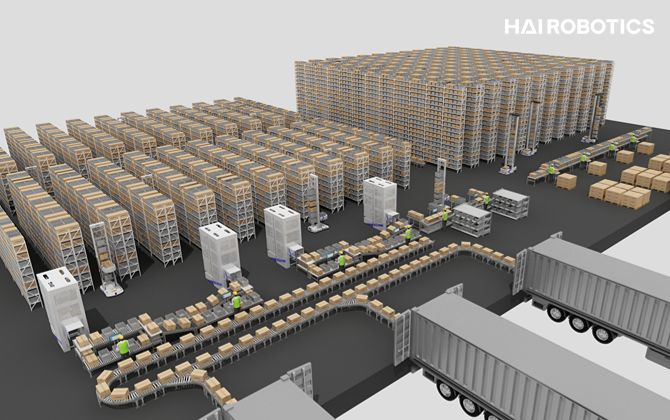
Warehouses are the beating hearts of supply chains, with order picking serving as the lifeblood that ensures a crucial rhythm is maintained. Amid the complexities of warehouse operations, order picking holds a profound influence on profitability and customer satisfaction outcomes—an efficient and accurate order-picking process is integral to maintaining a competitive edge.
"Don't ever underestimate the importance of accurate order picking," proclaim warehouse experts. From the outside, it may look like a mundane task. Yet, it accounts for up to 55%-60% of the total warehouse operation costs[1], justifying the push for optimizations. Read on if you belong to the tribe of warehouse managers, supply chain professionals, or frontline pickers seeking to upgrade your order-picking game with an array of tips, strategies, and optimizing practices tied to warehouse order picking.

Understanding Order Picking Processes
Order picking refers to the operational practice of selecting products or items stored in a warehouse to fulfill customer orders. Breaking down the process of order picking is akin to peering into the engine of a well-oiled machine.
-
Key Components
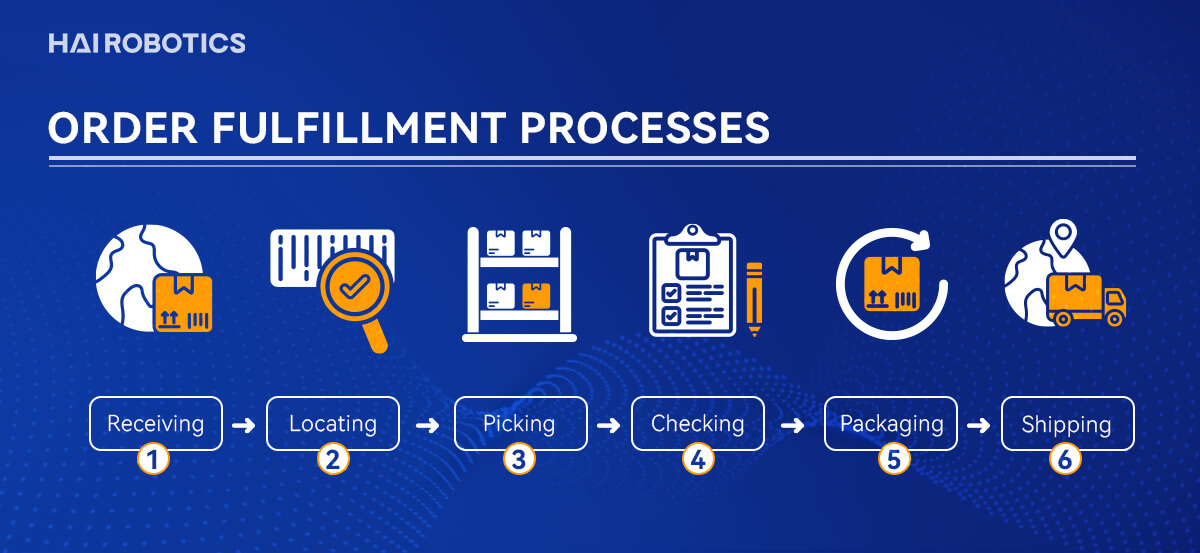
The gears of order receiving, item location, actual picking, and eventual packing for shipment work together with mechanical precision to meet the order demands. In order fulfillment, these steps are vital and directly affect an organization's service level, customer satisfaction, and overall profits.
-
Receiving: This is the initial stage in which goods arrive at the warehouse and are counted, inspected for damage, and entered into the warehouse management system (WMS).
-
Locating: Stored goods are properly organized to make the order-picking process more efficient and easier. Moreover, to fulfill specific needs and objectives, the majority of warehouses employ robotic systems for precise positioning and identification.
-
Picking: Using the warehouse management system (WMS), pickers receive order lists typically displayed on handheld devices. This information shows the exact product location, enabling them to locate items in the most efficient route possible.
-
Checking: To minimize mistakes, the picked items are placed through checks consisting of barcoding, scanning, or sometimes a physical count.
-
Packaging: The selection of packaging materials should carefully weigh cost-effectiveness against product safety. While cushy packaging can help protect goods, excessive use can lead to unnecessary additional costs.
-
Shipping: The packed goods are dispatched to their respective delivery locations using the most cost-effective method possible.
 Striking a best-practice tempo in order fulfillment is rooted in recognizing every element involved in the order stream. Strategically organizing these stages can facilitate smoother transitions between tasks. For instance, Robots provided by Hai Robotics can swiftly transport items to skilled workers for integrated picking and packing, ensuring swift and accurate order processing and dispatch. By implementing robotics-driven operations, CIRRO Fulfillment, a global e-commerce fulfillment company, has enhanced workforce efficiency by an estimated 30%, with a maximum daily outbound volume of up to 21,000 items. This innovative approach minimizes handling time and boosts operational capabilities, yielding quicker delivery and higher customer satisfaction. The overall shopping experience is thereby expedited and seamless.
Striking a best-practice tempo in order fulfillment is rooted in recognizing every element involved in the order stream. Strategically organizing these stages can facilitate smoother transitions between tasks. For instance, Robots provided by Hai Robotics can swiftly transport items to skilled workers for integrated picking and packing, ensuring swift and accurate order processing and dispatch. By implementing robotics-driven operations, CIRRO Fulfillment, a global e-commerce fulfillment company, has enhanced workforce efficiency by an estimated 30%, with a maximum daily outbound volume of up to 21,000 items. This innovative approach minimizes handling time and boosts operational capabilities, yielding quicker delivery and higher customer satisfaction. The overall shopping experience is thereby expedited and seamless.
-
Performance Metrics
In the world of warehouses and supply chains, inefficient processes can cause a domino effect of delays that slow everything down―from production to delivery―ultimately leading to disappointed customers. To achieve optimal efficiency in the order-picking process, several Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) should be utilized, such as picking accuracy, picking rate, fill rate, and other related metrics.
-
Picking Accuracy: This involves the accuracy with which items are picked, often expressed as a percentage. A high accuracy rate stands for fewer mistakes/returns, thus better performance.
-
Picking Rate: This measures how quickly individuals or teams can pick orders within a specific time, often calculated as items picked per hour or orders completed per hour. Rapid picking rates can indicate efficiency, but accuracy must not be compromised.
-
Order Fill Rate: This measures the number of orders filled with the requested items. It's usually expressed as a percentage of the total orders filled. A high order fill rate indicates efficient inventory management and picking process.
-
Order Cycle Time: This KPI calculates the time taken from when an order is received to complete picking it. Measuring this time can help identify sources of delay in the picking process and find ways to improve efficiency.
-
Items Picked First-time Right: This index evaluates the proportion of orders that are picked correctly the first time without any need for amends or additional checks. This results in time efficiency in the picking process.
-
Percentage of Wrong Items Picked: This KPI shows the proportion of errors in the picking process by evaluating how many items were picked incorrectly. The goal is to minimize this value to greatly increase efficiency and picking accuracy.
Every company typically tailors these KPIs to meet the unique demands of its operations and the prerequisites of its industry. For instance, JD Logistics, a global 3PL company, successfully managed over 100,000 SKUs with 100% picking accuracy using ACR systems from Hai Robotics. Similarly, Avenue Shops, a USA retail company, experienced a substantial impact on order fulfillment after implementing Hai Robotics' automation solution, boasting a 65% surge in daily shipped orders. These indicators serve as a basis for enhancing operational efficiency in order picking, assisting us in identifying the best solution providers.
Choosing the Right Order Picking Strategy
The selection of an optimal picking strategy is crucial for enhancing the efficiency of the order-picking process. It encourages scalability and boosts customer satisfaction by ensuring fast and accurate order dispatch. To achieve this precision, we need to initially understand and evaluate various picking methods, and then seamlessly integrate these strategies into existing systems for heightened efficiency and expedited order fulfillment.
-
Different Picking Methods:
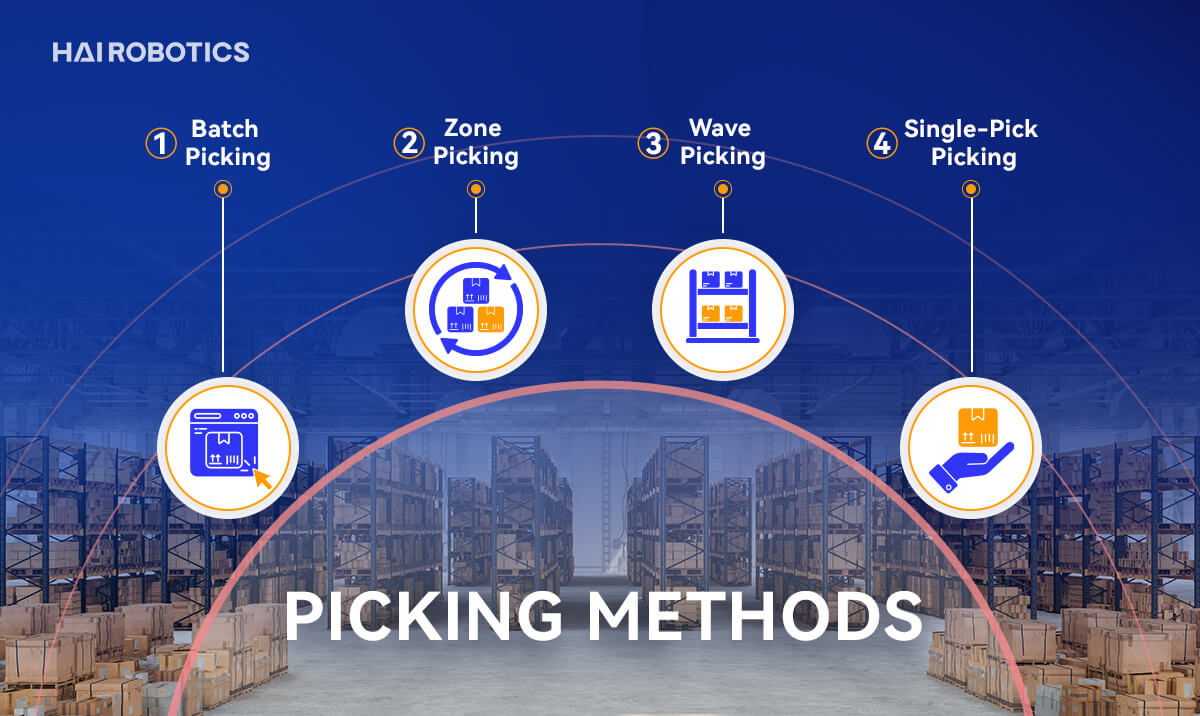
The performance and efficiency of order picking are greatly influenced by different methodologies that aim to reduce time and errors, thus increasing overall efficiency. Various picking methods cater to diverse business needs depending on factors such as order frequency, volume, warehouse design, and types of goods handled, among others. These methods include:
-
Batch Picking: A method that groups orders into “batches” based on SKU similarity and the similarity of each order’s characteristics, which proves valuable for sizable companies processing thousands of similar orders daily. Batch picking enables the picker to collect SKUs for multiple matching orders simultaneously, minimizing travel time.
-
Zone Picking: Alternatively known as the pick-and-pass method, divides the warehouse into distinct zones and assigns pickers to each. Each picker concentrates on collecting items only from their allocated zones, eliminating aimless ground coverage and complex picking routes. As orders traverse across the zones, different items from each area are incrementally collected until the order achieves full completion. This method of the labor division remarkably enhances warehouse processes and resource distributions.
-
Wave Picking: It is a systematic approach to order fulfillment where orders are classified and processed into designated 'waves', based on attributes such as shipping carriers or departure times. Originally assembled as individual sets, these orders are later consolidated into singular consignments. Wave picking seamlessly tackles scheduling control, labor distribution, and shipping organization - offering benefits, especially for businesses grappling with large or volatile daily order volumes.
-
Single-Pick Picking: With its simple framework, a designated worker is devoted to sourcing every item required for each individual order. Though efficiency can be a challenge when dealing with a high volume of orders, its simplicity makes this system direct in achieving its purpose.
-
Integration with Systems:
Your order-picking strategy would swiftly fall into chaos without seamless integration with contemporary warehouse management systems (WMS). System integration ensures efficient communication, aligns responsibilities simultaneously, and overall consolidates workflows better. Here are some steps to follow:
-
Analyze Current Systems: Start by identifying the limitations and inefficiencies of the current system. Then, pinpoint areas that need improvement and determine the most suitable picking strategy. Utilize key performance indicators (KPIs), such as order accuracy and picking speed, to guide this process.
-
Implement Software: Software is the brain of the warehousing system—handling tasks like SKU records, their quantities, and their storage locations. It documents inventory information at receiving, then directs putaway, slotting, picking, packing, order consolidation, shipping, and all other processes related to picking orders. With insights gathered from real-time inventory data, you can refine and implement new picking strategies.
-
Develop Modern Interface Standards: It ensures the interconnectedness of existing platforms or subsystems such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP), E-commerce platforms like Shopify, transportation management systems (TMS), and more. Thus, the entirety of the supply chain remains in great synergy.
-
Employee Training: Today's WMS can communicate real-time status on orders, inventory, and individual picker performance. Leverage technologies like radio-frequency identification (RFID), barcode readers, or wearables that can offer real-time updates on inventory levels and picking tasks. Warehouse employees should be trained to understand order picking paths, the use of equipment, and how to navigate the software.
-
Continuous Improvement: Once the strategy is implemented, always pursue continuous improvement. Use key performance indicators (KPIs) to establish a basis to gauge improvements or potential issues. In this process, consistently revisit your picking strategies, adapt as your warehouse grows, and align with emerging technologies.
Implementing Best Practices for Order Picking
How can Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) be maximized during the order-picking process? Assembling an efficient and minute scheme logistics environment can radically transform warehouses into profitable centers of productivity. With optimized processes, innovative technology, and the most powerful team, warehousing operations run smoothly and efficiently, resulting in significantly increased profitability.
-
Layout and Organization:
A warehouse's efficient movement of goods directly correlates to its effective layout and organizational methods. A disorganized warehouse can cause complications that slow down order picking, while a well-structured system can enhance both speed and accuracy.
A strategically designed, well-organized layout, optimized for ideal picking paths, minimizes movement and thus enhances picking speed. For optimum efficiency, items with high turnover rates or those often sold together should be placed close to each other and in easily accessible zones. Prioritizing this strategy, known as the ABC Analysis approach, has been shown to improve retrieval efficiency, reducing picking time by 20% or more[2].
To cater to different stages of fulfillment – from packing, sorting, to shipping – aim to establish staging areas designed for these specific product types. An organized system like this accelerates order preparation, cuts down on errors, and ensures fluidity within the fulfillment process.
Furthermore, an orderly, secure, and clutter-free workspace can boost productivity and mitigate risks, such as personnel injuries or machinery failure. A study conducted by Staples Corporation underlines this point, with 94% of workers testifying to heightened productivity in a spick-and-span environment, while 77% asserted that the quality of their output was superior in well-kept conditions[3]. Infrastructural cleanness - even slight improvements - in a warehouse setup can yield remarkable productivity advantages when the workforce perceives these changes as manifestations of their overall safety and appreciation.
-
Technology and Equipment:
Beyond the physical layout of warehouses, advancements in technology and specialized equipment serve as influential tools in the modern age. These innovations aid in boosting productivity, minimizing expenditure, and streamlining the process of order fulfillment, establishing an unparalleled edge in warehouse operations.
-
Voice Picking Systems: Allowing for efficient, hands-free, and paperless operations, the voice-guided picking system equips operatives with real-time instruction headsets. Via vocal cues, these bespoke devices direct order pickers through each step, guiding them to specified locations while providing imperative details about the product selection and quantity specifications.
-
Pick-to-light Systems: They are composed of a series of modules with colored lights and display screens attached to inventory locations. Lights illuminate targeted pick quantities and may display a container identification number so the worker knows where to deposit picked items. When picking tasks are completed, the light turns off. These systems streamline the picking process by 30%-50% with 99.9% accuracy[4].
-
Barcode Scanner Systems: Creating barcodes is a process of generating unique codes used for the efficient management and tracking of inventory items. Barcodes are graphical representations of data that can be easily read using barcode scanners and corresponding software. This approach records the movement and identification of their inventory accurately and quickly, leading to enhanced inventory control, and operational efficiency.
-
Radio Frequency (RF) Picking Systems: They make use of wireless devices that communicate via radio frequency to guide workers through warehouse processes such as picking, packing, and restocking. Workers carry handheld RF devices that display item locations and quantities to pick, based on information in the warehouse management software. As each task gets completed, updates are transmitted back to the central database through RF.
-
Smart Robotics Systems: Robots are designed to complement manual picking processes and collaborate with order pickers. For instance, a robot can autonomously navigate to a picking zone, where a picker places an item into a bin or tote attached to the robot. The robot then independently navigates to the next zone and this process continues until all items are picked. The deployment of intelligent systems like Autonomous Guided Vehicles (AGVs), Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs), and Automated Case-handling Robots (ACRs)—each beneficial in unique applications—enhances operability, reduces strain in picking, and significantly increases safety. Moreover, combining these systems can improve efficiency. Take the HaiPick System 3 provided by Hai Robotics for example. By integrating this state-of-the-art generation of ACRs with self-developed Fast-transit Companion AMR robots, companies can achieve a more flexible layout and maximize their facility's space utilization.

-
Empowering Your Picking Team
First-class warehousing operations depend on various factors, yet the importance and efficiency of the picking teams cannot be denied. Investing time, energy, and resources into developing these teams can significantly accelerate a company's overall logistical success by increasing labor productivity, improving safety, and enhancing worker engagement.
-
Training and Development:
Savvy warehouse owners understand that depth of knowledge and mastery amongst pickers warrants achievement. Vastly, this necessitates diligent attention to training and continued development. Research conducted by the University of Moratuwa found that training warehouse workers was a top-three factor affecting the efficiency of warehouse picking[5].
Primarily, training must be comprehensive and span several areas—supplementing the learning environment that helps pickers become assets rather than just workers. To achieve this, employing methods like structured on-the-job training and simulation-based learning proves beneficial for understanding warehouse layouts, picker routes—often aided by the Warehouse Management System (WMS), and inherent challenges that hinder efficiency[6].
-
Ergonomics and Work Environment:
Optimized performance is undeniably bound to physical well-being – which jumps to why ergonomics stands significant. Nurtured tasks lighten injury pains hence sustaining productivity all-serving for heightened morale and higher economic results.
Now attaining this requires a strategic focus on various ergonomics interventions, packed tightly around designed equipment/initiated work practices. Structural changes, like ergonomic lifts, and adjustable workstations, also aim toward longer effectivity. For instance, the HaiStation, provided by Hai Robotics, utilizes an ergonomic design where workers and HaiPick robots operate interconnectedly, and goods can be sorted on the conveyor line without unnecessary movements. This streamlines operations and enhances warehouse efficiency.
Overall, ergonomic improvements such as user-friendly workstations and appropriately timed breaks ensure less fatigue while driving productivity higher.
Summary:
Cracking the code for supreme supply chain management presents numerous trials and setbacks. However, practices bolstered by precision, efficiency, and innovation can exponentially progress an organization's potential when implemented appropriately.
As complex as it sounds, consider this as a gardener' work: Careful nurture and patience generate productive crops, compose fertile realities! Exploiting this robust array of tested strategies paves the way for gratifying results of efficiency and profitability to heed the optimistic lure of your revamped warehouse workings swiftly. a relentless pursuit of update synthesis aids in maintaining picking operation uptimes.
For more information on warehouse order picking and how to optimize your warehouse processes, please feel free to contact Hai Robotics.
Footnotes
[1] James A. Tompkins, John A. White, Yavuz A. Bozer, and J. M. A. Tanchoco. Facilities Planning: Fourth Edition. New York: Wiley, January 2003.
[2] Carlos Abel Santa Cruz Puente, Joe Pui Lo Wu Gamarra, and Rafael Mauricio Villanueva Flores. Application of the Abc Methodology to Reduce the Delay of Sales Orders in A Company Warehouse in Barranca City. 4th South American Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, May 2023.
[3] Sophie Rioch. 94% Of Workers Feel More Productive In A Clean Warehouse. ICE Services Group Ltd, January 2021.
[4] Pick to Light | Solutions Guidd | Solutions Community. MHI - Material Handling Industry, May 2005.
[5] Oliver Munro. 10 Warehouse Order Picking Tips: Optimise Your Processes. Unleashed Software, December 2022.
[6] Tufano, A., Accorsi, R. & Manzini, R. A machine learning approach for predictive warehouse design. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 119, December 2021.

